The SAP HANA platform has become a future-proof platform for SAP innovation development. It combines various data processing methods: transactional, analytical and functional ones, supporting application logic, directly in the cache. Such an architecture enables the execution of demanding business processes in real time, while supporting OLAP and OLTP processing for data structures. It represents the fastest growing product in SAP’s history significantly influencing the direction of application development. To run this new digital core for SAP systems, a modern in-house or vendor’s IT infrastructure is required. IT departments face the challenge of consolidating the resources required to maintain traditional SAP ERP systems and SAP Business Warehouse (SAP BW), while securing the investment against a possible migration to S/4HANA.
The launch of new functionalities delivered with the HANA platform version 2.0 may significantly influence the directions of infrastructure development, as well as the planning of use of available resources. The main changes introduced by the software manufacturer consist in increasing data security, flexibility, and lowering storage costs in the context of TCO.
Furthermore, it is hard to overestimate the parallel development of the embedded architecture of the SAP HANA eXtended Application Services (XS) server, classic and advanced data models, functionalities in the area of “tenants" or development and administration tools such as: SAP HANA studio or HANA cockpit.
Reducing TCO
When planning the development of an existing infrastructure, as well as a new implementation or migration of currently owned systems to the HANA platform, TCO or license cost management should be considered. New data storage functionalities will address the following challenges:
- The growth of the data volume forces the expansion of the SAP HANA system, leading to the achievement of the platform limits;
- High cost of in-memory licenses for non-SAP solutions using the SAP HANA platform;
- The growth of the data volume affects the query execution time and the performance of the entire HANA platform.
By reducing the amount of data that needs to be stored in expensive DRAM, you can significantly reduce the cost of infrastructure required to maintain that data, while continuing to provide consistent access to it with satisfactory performance.
With the introduction of the SAP HANA Data Tiering solution, SAP enabled data to be deployed based on its value and access time. In this configuration, the most important data, i.e. the data that requires immediate access, is stored in the operating memory, while less important data is moved to the medium that provides the best cost/performance ratio. New functionalities in this area have been specified by the manufacturer using terms with data temperatures assigned to them: Hot Data Tiering, Warm Data Tiering and Cold Data Tiering.
SAP HANA Data Tiering
Hot Data Tiering
All applications have the same in-memory storage capabilities. For critical data that requires real-time access. Nonvolatile memory (NVM), also known as SAP HANA persistent memory (PMEM), provides more capacity in addition to the used operating cache of the server. PMEM offers a lower total cost of ownership and faster database startup time after shutdown than DRAM, but it does not replace it because DRAM is still required in SAP HANA systems.
Warm Data Tiering
When the data set and access to it become less critical, the native mechanisms of SAP BW on SAP HANA and SAP BW/4 HANA can be used to “cool" the temperature of the data and move it to a disk solution that provides performance similar to the performance when the data is maintained in DRAM. The Data Tiering Optimization (DTO) modeling tool manages the classification and relocation of data between SAP HANA and the Native Storage Extension (a new feature released with SAP HANA 2.0 SP4). NSE is a disk-based space table extension for columnar tables in SAP HANA. Instead of loading an entire column from a table when accessing data, only the necessary pages are loaded into the buffer cache.
For native SAP HANA applications, the function of storing less relevant data is offered by the Dynamic Tiering extension. This functionality is easy to implement and manage, but it does not support some SAP HANA features, such as geospatial features. In this solution, the Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) tool facilitates data tiering by enabling rule-based transfer of less critical data.
For Business Suite on HANA and S/4HANA solutions, a mechanism called Data Aging determining the value of data based on attributes has been implemented. The mechanism enabling Paged Attributes currently can only be run on selected objects. Periodic job flows verify information about expired objects by dumping them to disk. In this configuration, the tables are divided into partitions with “hot" current data and “warm" historical data.
Cold Data Tiering
Just as all data in the “hot" and “warm" tiers resides in the SAP HANA database, data in the “cold" tier resides in external systems such as SAP IQ, SAP HANA Vora or Hadoop. DTO enables the lowest temperature data to be classified and transferred to an external solution. For the Business Suite on HANA and S/4HANA, a similar function is performed by the SAP Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) tool that allows you to specify attributes on objects that are the basis for transferring data to the external solution. Both mechanisms provide access to the transferred data.
The above mechanisms should become part of the migration strategy and new implementations from the very beginning of the project. Their use can significantly reduce the costs of IT infrastructure maintenance.
Another option available to reduce the cost of maintaining a hardware platform equipped with a large amount of cache is the use of server solutions with the Intel Optane option. This technology allows the use of slower memory chips embedded in DIMMs. PMEM (Persistent Memory) is an innovative memory technology that uniquely combines high capacity and data persistence with an affordable price. It can help companies innovate thanks to increased capacity and modern memory modes, lower overall total cost of ownership while maximizing VM density, and improve memory security with automatic hardware encryption.
PMEM modules use the same bus, identical channels and function as a DRAM replacement. They are not as fast as DRAM modules. However, given the price/capacity ratio and the option to increase capacity beyond what DRAM can offer, the TCO is significantly lower than that of DRAM. An additional advantage of the solution is that data is retained in PMEM memory during the server restart. There is no need to reload large volumes of data during the system startup, which helps reduce system downtime.
Data security
With the development of the SAP HANA platform, the manufacturer provided new capabilities for data replication to backup systems. The use of the mechanism not only increases data security, but also allows you to optimize the way data is accessed, e.g. for analytical purposes. Data is replicated in real-time to a second standby HANA backup system. The SAP HANA system version (2.0SP3) additionally provides a mechanism for operating the standby node in read-only mode. This functionality can be used for reporting by connecting a data source from the standby node, reducing the load of the primary node. The read-only mode on the node blocks any manipulation of this data. Data can be permanently preloaded into the auxiliary system memory to minimize the recovery time objective (RTO).
In SAP HANA 2.0 SP4, the software manufacturer introduced the possibility of replicating the system to more auxiliary systems. The functionality can be used in designing a DRC procedure (a backup data center), and also to overcome the impact of wide area networks on access to data in different geographical locations. This solution allows you to place the HANA platform in any location and replicate data from the production system to it. Any analytical operations that do not require the source data to be changed can be performed locally on such replicated data. Data can be modified only in the central system.
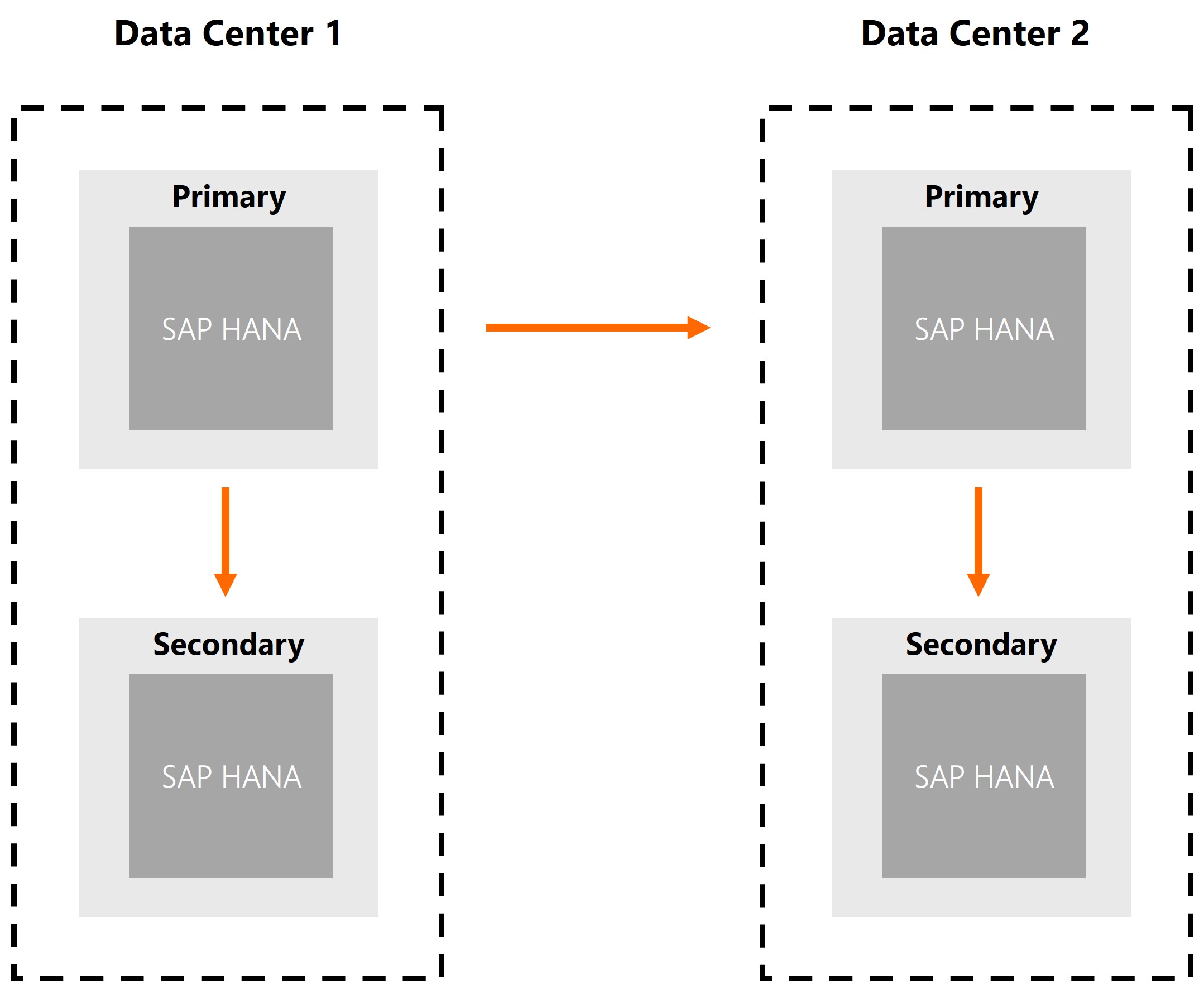
System replication to auxiliary systems in SAP HANA 2.0
SAP HANA replication modes
- Synchronous on disk (mode = sync): the transaction is validated after the log entries have been saved to the primary and auxiliary systems;
- Synchronous in-memory (mode = syncmem): the transaction is validated after the auxiliary system receives the logs, but before they are saved to the disks. This type of synchronization is recommended in scenarios where both nodes are placed in a single network characterized by high bandwidth and low access times;
- Asynchronous (mode = async): the transaction is validated after sending the log entries without any response from the auxiliary system;
- Full synchronization: full synchronization is supported by SAP, but cannot be configured with high availability software.
Anonymization and data masking
The new version of the platform enables data to be used for analysis and machine learning scenarios in the context of GDRP and other privacy laws. With k-anonymity and differential privacy algorithms, data is sent in such a way that the result remains statistically valid, but can no longer be linked to individuals. Additionally, you can add a custom definition of anonymization views, access reporting views, and take advantage of integration with an authorization framework.
SAP HANA native dynamic data masking is available in SAP HANA and SAP HANA Cloud. This feature protects row-level data with data masking in tables and views. Data is not replicated but masked on the fly if unauthorized users access it. Masking in SAP HANA is highly configurable and can be customized according to requirements.
Native application server
Although SAP S/4HANA and SAP BW/4HANA are supported by the NetWeaver application server, SAP HANA also has its own built-in, “native" application server. The first version was based on the SpiderMonkey JavaScript engine. It had a minimum size and was called SAP HANA eXtended Application Services, or XS for short. Since this architecture had its limitations, a completely new application server was added with the new release, this time based on the open-source Cloud Foundry. The local distribution of Cloud Foundry was integrated with the in-memory platform and renamed XS Advanced (XSA). The original XS implementation is now labeled “classic.”
The application server functionality is used by the developer in a design application called SAP Web IDE.
SAP HANA Cockpit 2.0
In the new version of the SAP HANA platform, the manufacturer recommends using a new version of a centralized cockpit based on the express version of SAP HANA, with its own advanced XS application server infrastructure and comprehensive and easy-to-use system management tools.
The new cockpit enables us to manage entire landscapes of SAP HANA systems as well as individual systems. The integration of HANA systems with SAP HANA Cockpit 2.0 does not exclude the possibility of further use of the well-known solution based on the Eclipse environment – HANA Studio.
Even more novelties
The list above is the smallest selection of what’s new in SAP HANA 2.0. The platform enables organizations to adopt security rules and standards and provides the tools necessary to innovate in today’s business environment. Organizations can implement demanding solutions that will be used to gain an information advantage. The ease of configuring, managing and monitoring security measures allows you to stay ahead of the competition while meeting privacy, regulatory and compliance requirements. The manufacturer continues to support its customers in maximizing the benefits and protecting their investment by charting the way forward.
Future releases are planned to include not only stability and quality improvements but also innovations that reduce the total cost of ownership and increase usability as well as improved machine learning capabilities with new PAL algorithms that are supported by Python 3. Further upgrades to the native storage extension will be available to complement SAP HANA’s Big Data capabilities. In the coming years, the SAP HANA platform will be integrated with future SAP products as a smart enterprise platform.
SAP HANA in the All for One offer
All for One Poland offers a full range of services related to launching HANA (including migration to SAP HANA) in the following scenarios:
- SAP HANA for SAP Business Suite (SAP HANA for SAP ERP/ CRM/ SCM),
- SAP HANA for SAP Business Warehouse (SAP HANA for BW),
- SAP HANA standalone,
- dedicated applications for SAP HANA.
We also offer:
- hosting SAP HANA environments in All for One Data Centers,
- application development on the HANA Cloud Platform (HCP),
- services and solutions for migration to S/4HANA.

