Good planning tools
SAP has always been known for the quality of its planning tools. The flagship SAP ERP system (ECC) allows the planner to plan in long, medium and short term horizons. The main components offered by SAP in the ERP system (ECC) are the tools for:
- S&OP (Sales and Operation Planning) long-term planning tools – the so-called product group-based planning and the so-called flexible planning.
- LTP (Long Term Planning) planning and simulation planning
- demand planning and modelling, e.g. Demand Management (DEM) sales forecast consumption strategy,
- Master Production Scheduling (MPS),
- Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP) and balancing.
The standard tools used for production planning in SAP ERP offer and support MRP planning in MRP2 standard – material demand planning and initial capacity utilization. Possible balancing of the production plan against the availability of individual resources is performed in a separate step.
MRP methodology
The primary planning assumption is the execution of the so-called MRP runs where the system performs material requirements planning for all technological levels from a finished product to raw materials, simultaneously creating capacity requirements. According to the MRP2 methodology, we can make production plans covering all of the company’s resources (materials, purchases, sales, production capacities, technological data, machines, etc.). The main planning tool used to create production plans with the so-called capacity levelling were symbol-based or graphical planning boards. In pursuit of greater automation and flexibility of planning processes, the above-mentioned tools were complemented by advanced manufacturing planning capabilities offered by SAP APO.
How to start SAP APO
So far, SAP APO has been launched as a separate system installation. It has been treated as a part of the Supply Chain Management (SCM) system. This was required primarily by the assumptions related to the method of processing huge amounts of data and the relationships between them. It was necessary to use dedicated engines, the so-called accelerators working with data stored in memory, maximally reducing the main bottleneck of processing large amounts of data, which is the time of access to a traditional disk database. The introduction of the HANA database (In-Memory database) by SAP has enabled the implementation of solutions related to advanced planning directly in the ERP system (ECC).
The main components of the APO system in the stand-alone version were:
- DP – Demand Planning
- SNP – Supply Network Planning
- PP/DS – Production Planning / Detailed Scheduling
- GATP – Global Available To Promise
By introducing the new S/4HANA system, SAP offered the possibility to launch advanced, detailed production planning (APO PP/DS component) without the need to install an additional, dedicated SCM system and server. Therefore, planners can benefit from a completely new philosophy of handling planning processes supported by SAP through the use of so-called heuristics (ready-made algorithms, predefined to solve specific planning problems).
Unrestricted development of the system
As a standard, SAP also offers modification and creation of new sets of algorithms, which allows planners to develop, modify and adjust their planning philosophy according to the strategies adopted at a given time by the company. This tool frees the planner from a certain structured, perhaps unnecessarily stiffening approach compliant with the MRP2 methodology, opening up a wide array of options and offering completely new tools available from the ERP (ECC, S/4HANA) system.
If, after all, the configuration option did not exhaust business requirements, SAP also provides secure software for brand new heuristics. Thanks to such an approach, we are able to develop the system practically unlimited while ensuring security and correctness of planning results provided by other heuristics.
The Advanced Planning module in S/4HANA is not a direct “clone" of SAP APO functionality. Until now, the APO system had an independent data structure. Data exchange took place via the main interface (so called CIF). APO PP/DS creates, among others, basic data of products, resources, production structures (PDS or PPM), etc.
Master data modelling
In S/4HANA the master data is modelled in one, main place of the system. This is in line with the approach of simplifying the architecture of the system and the main assumption of “Single source of truth" – i.e. a single collection point and a single source for data analysis.
And correspondingly:
Material master data – we have the possibility to create a new tab “Extended planning". Checking the box “Advanced planning" and saving material changes starts the automatic procedure of creating product master data in PP/DS.
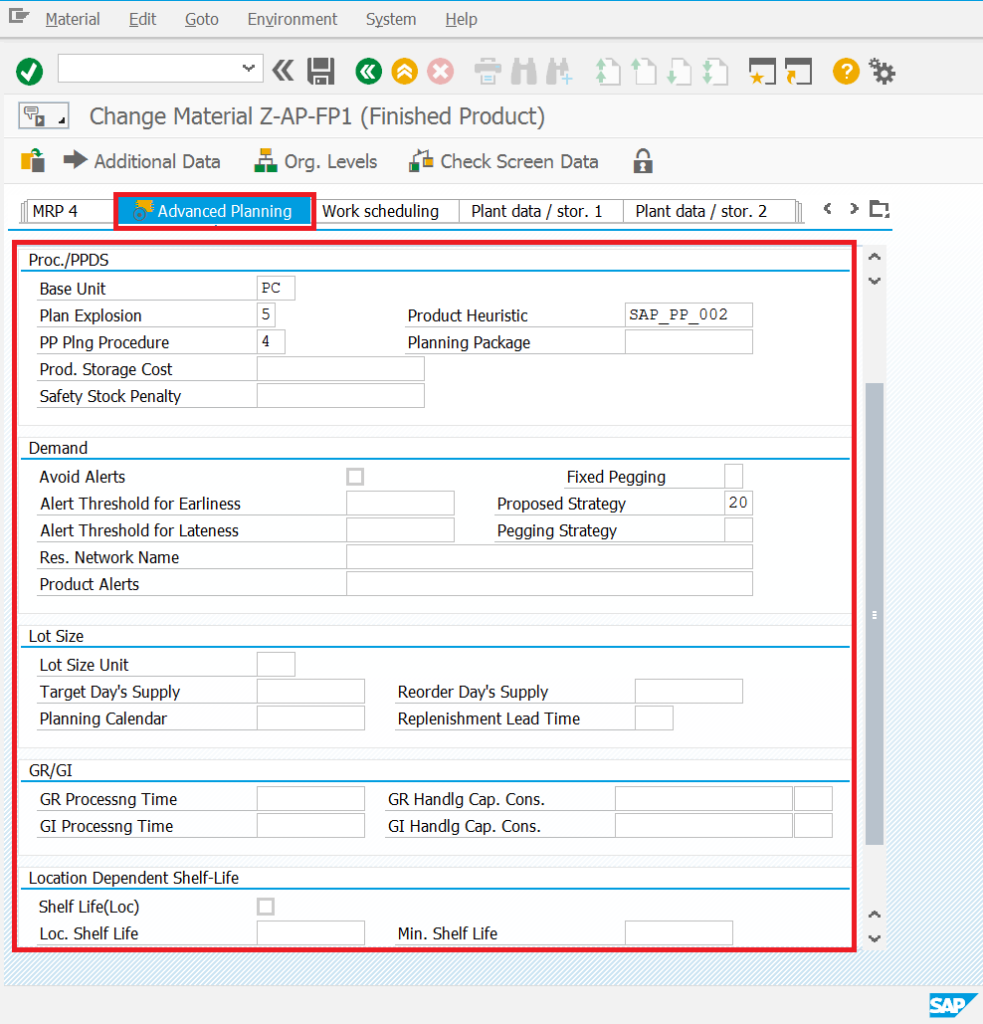
Material master data
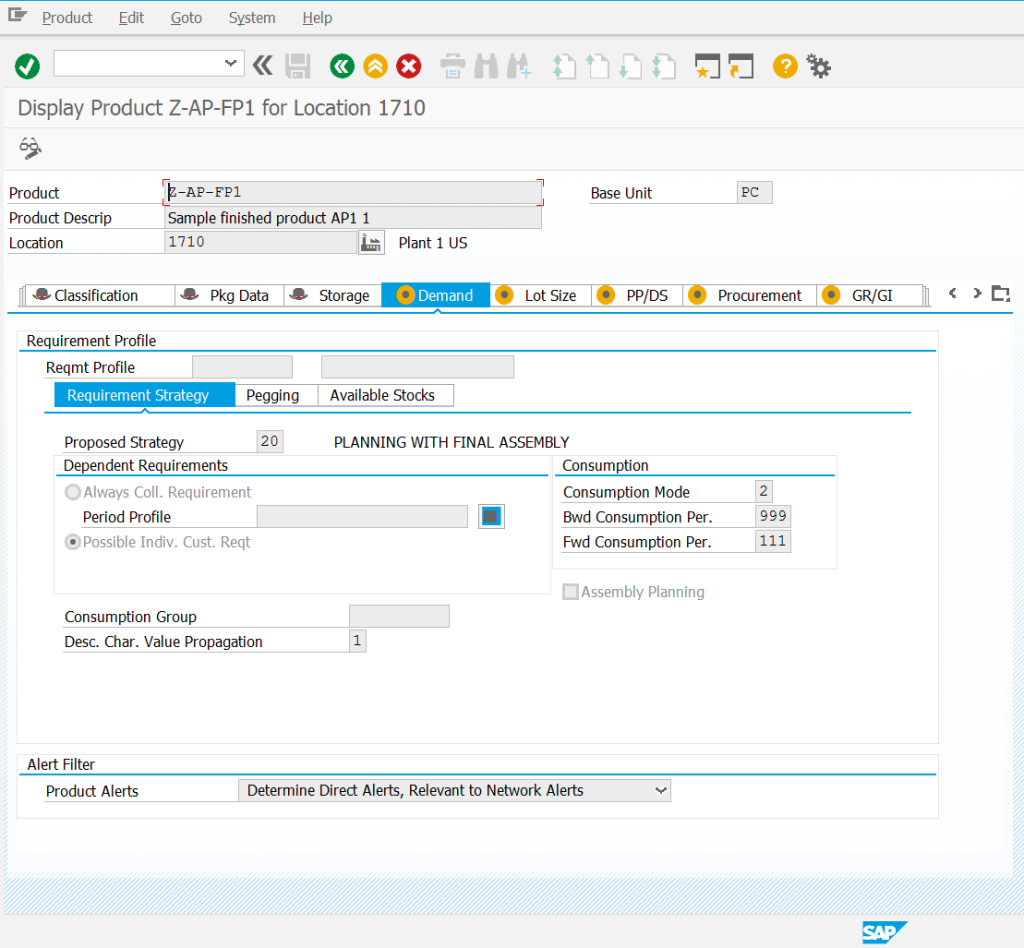
PP/DS product master data
Work centers – as with the material data, work center data are created as standard, just as in the case of SAP ERP (ECC), while selecting the new indicator “Advanced planning" automatically creates the resource master data in PP/DS.
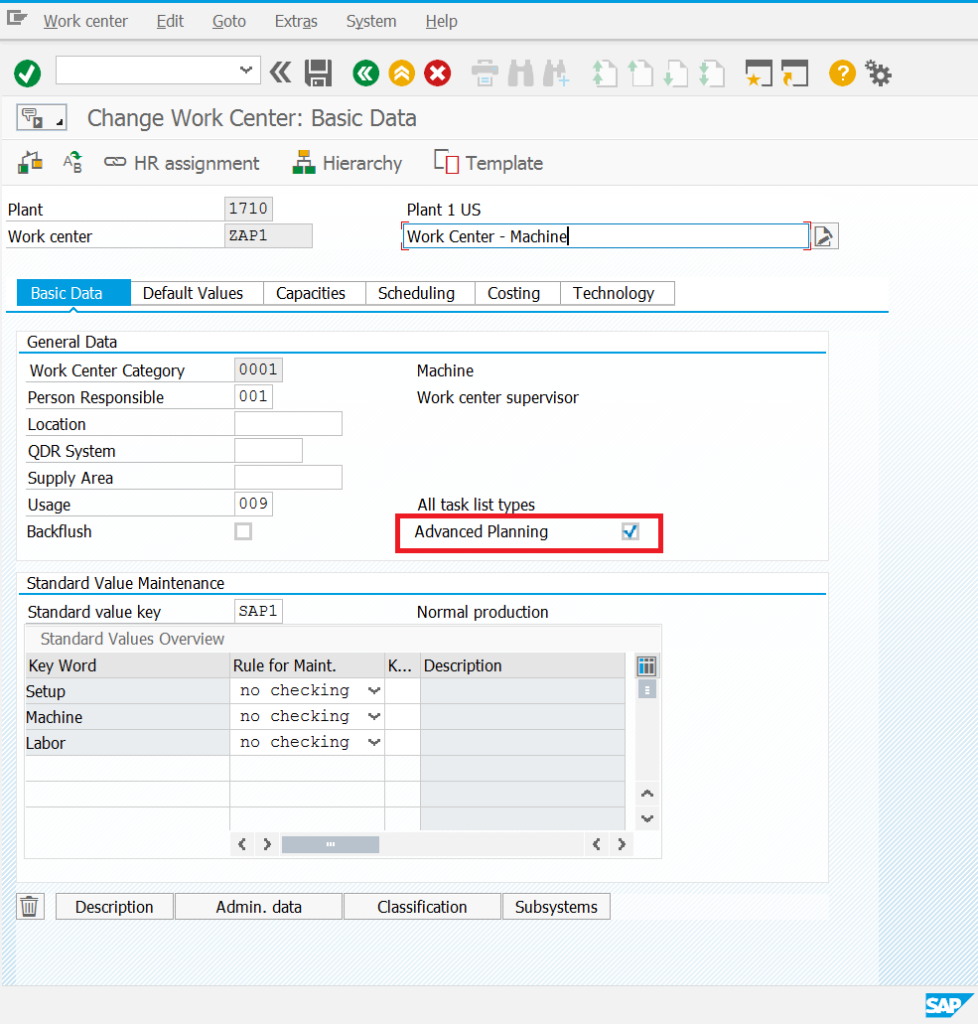
Work center
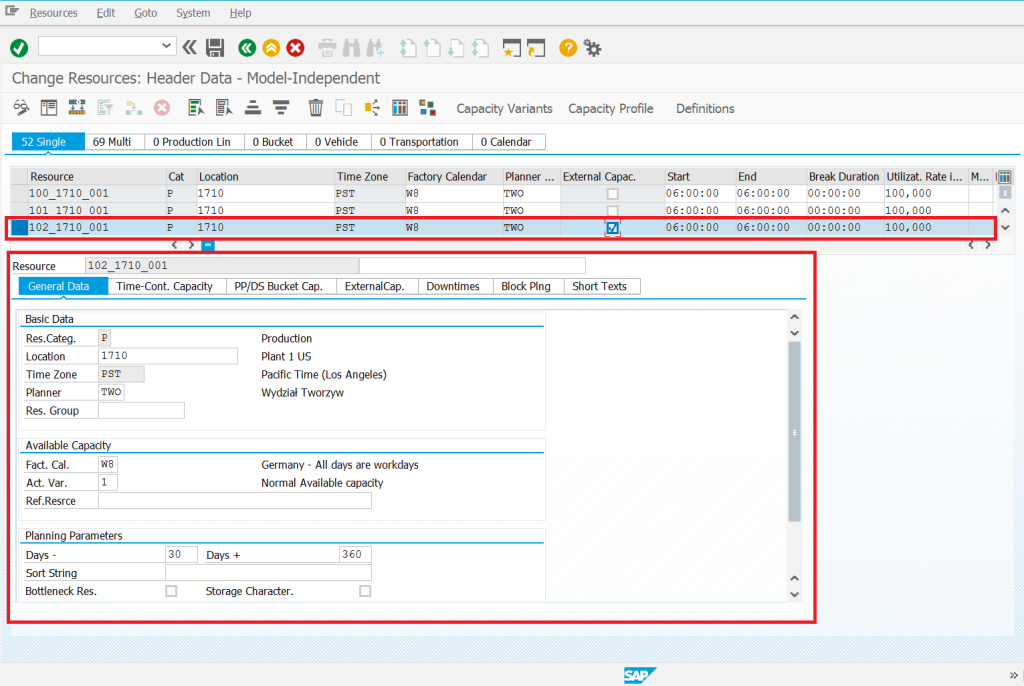
PP/DS resource
Production version – the basis for creating the production structure master data (PDS – Production Data Structure) is the conversion of production versions. Production versions were already used in SAP ERP and made it possible to unambiguously combine BOM material specifications with routing and technological operations into one specific model of product implementation. In S/4HANA we run a tool to convert production versions to PDS in the PP/DS module.
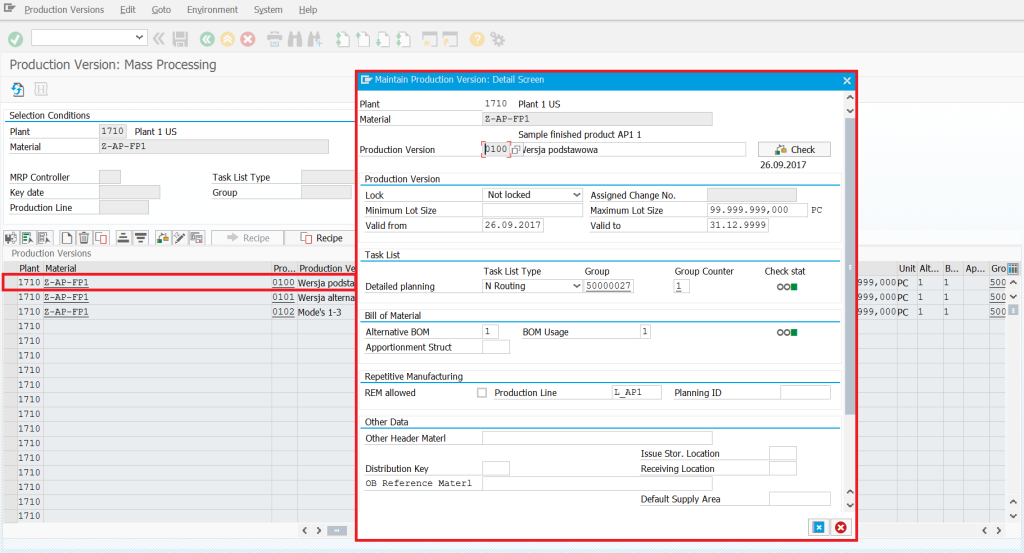
Production version
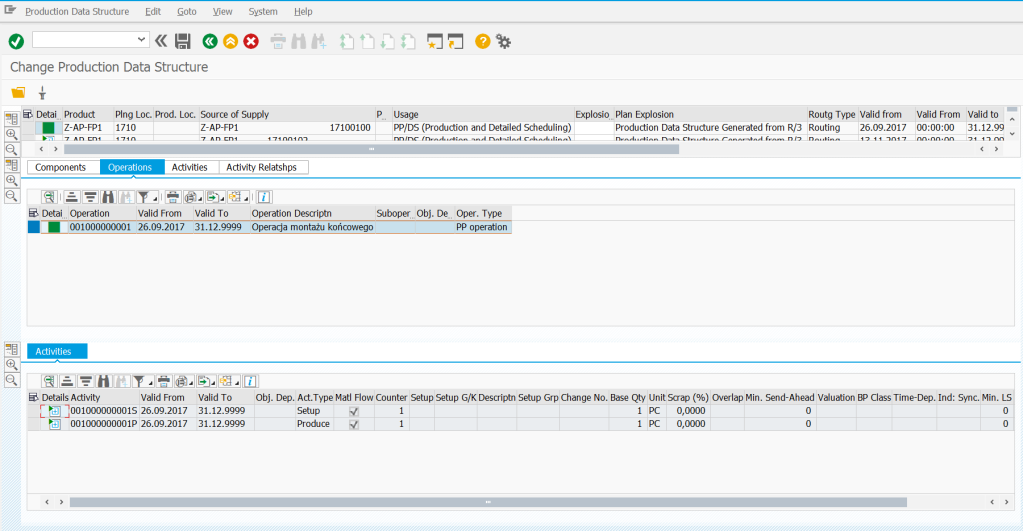
PDS in PP/DS
Planning in PP/DS
The planning process carried out in PP/DS uses the so-called heuristics – ready-made algorithms that plan and solve specific situations appearing in production plans. The system reacts dynamically, creating a system of alerts, which are handled through the so-called alert monitor. The tool is flexibly configurable. You can decide what type of events should be reported with the appropriate status and priority. Importantly, the user can configure the validity of the message data and the values (time/quantity) that will show the planning situation as information, warning or error. Due to the fact that in PP/DS we have the ability to create a plan for a minute or even a second, the planner can receive very targeted alerts related to possible disturbances in the production plan.
The functions of the extended planning module can be divided into two basic elements:
- production planning – related to the creation of planned orders and purchase requisitions, using mechanisms to create optimal sizes of production batches,
- detailed scheduling – connected with creating an optimal path and sequence of operations and orders on particular resources.
Production planning is a kind of “MRP process" in a standard SAP system. It can be set so that the system automatically performs the next steps, where each of them activates a different, specific method of planning and scheduling or optimization.
Examples of steps automatically taken by the system:
- the determination of MRP processing level codes,
- production planning – calculation of inventory and requirements,
- execution of automatic scheduling of the production queue due to dependencies and lead time problems at lower levels of the BOM structure of individual products (e.g. propagation of stable forward planning, when the date of demand for the finished product would mean that production orders for the intermediate product would have to be launched in the past),
- Optimisation for a given resource or group of resources, e.g. for queue setting using a refitting matrix.
Setting an appropriate queue of steps in a given run of the plan allows the planner to “assign" to the system the performance of typical activities that would have to be performed iteratively d in the standard planning. Importantly, the planning process and the possible further processing of this result, e.g. in the detailed planning table, can be carried out according to the specific version of the plan. The user can create several versions of the plan – that is, copy the actual planning situation into an inactive version, where you can try individual changes and their impact on the whole plan without any consequences. In this way, it is possible to perform simulations and select the appropriate path/method of steps before the plan is finally implemented and has an impact on other departments of the company. What is extremely important – the planner can change the available production capacity for the selected version of the inactive plan, which allows to simulate the feasibility of the production plan, for example, if we launch another shift or start working during the weekend.
Detailed planning
Detailed planning is based on the use of strategies and heuristics to balance production capacity. Preceded by appropriate modelling of resources as potential bottlenecks, it identifies the necessity and priorities for treating the planning of a given resource as a so-called finished plan.
In the PP/DS sub-module, SAP provides the user with a completely new set of tools. The most important ones are briefly listed below and (please treat this as a huge simplification) SAP standard transactions are assigned – as if they were the equivalents of the PP/DS sub-module. For people working in the SAP system on a daily basis, they will be nothing new, but such a comparison may be helpful in assessing how many novelties appear in the PP/DS module.
Online production planning process – equivalent of MD01, MD02 in SAP ERP. Additional elements are the possibility of defining the next automatic steps (heuristics) performed by the system. We not only plan inventory and demand, but we can also optimize and schedule resources according to defined strategies.
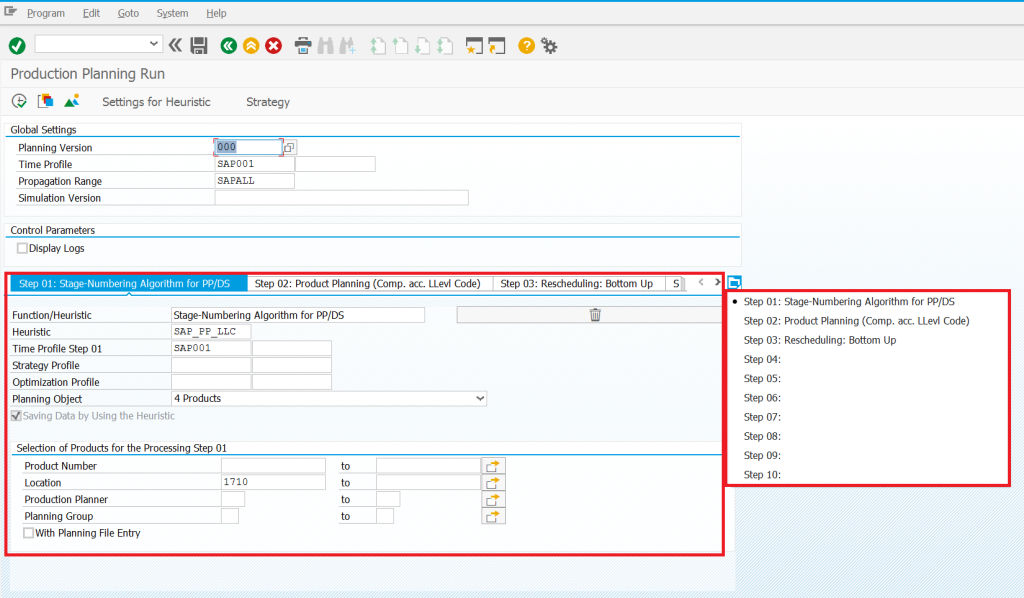
Planning of production in the background
Product view (planning situation including all elements of inventory, demand and admissions in the planning horizon) – MD04 equivalent in SAP ERP. Additional elements include the ability to run product heuristics and variables of heuristics, where the planner can dynamically change control parameters (batch sizes, replenishment strategies, scheduling of resources, etc.). – i.e. recalculate the current situation for a given material index with a highly developed MRP mechanism and to schedule these results in accordance with the adopted strategy. The system allows to go to the alert monitor, displays quantitative, timely and network alerts for given elements included in the list on an ongoing basis. The user can immediately create new planned orders, forecasts, etc. The user can also link the demand with the replenishment elements in accordance with own guidelines, creating so-called fixed pegging. Importantly, such links do not require make-to-order production mode (MTO).
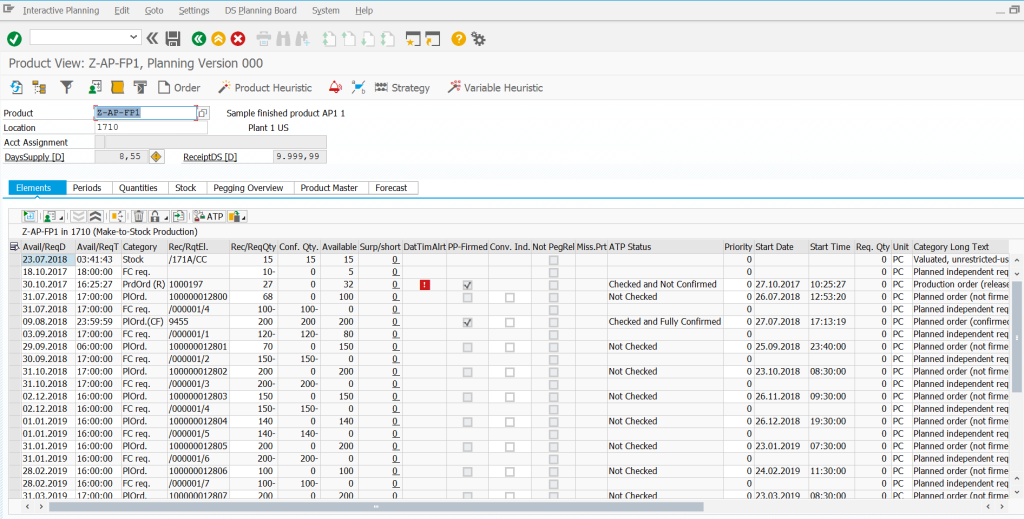
Product view
Product planning table – equivalent of MF50 – a sign planning board in SAP ERP. Additional elements are e.g. the possibility to dynamically choose what type of data (sub-screens) the planner wants to see at a given moment. You can simultaneously verify MRP elements from the product overview, resource charts from the detailed planning table, optimizer parameters, detailed planning heuristics, overview of demand relationships (the so-called pegging), production view – single elements, product view – quantity graphics, etc.
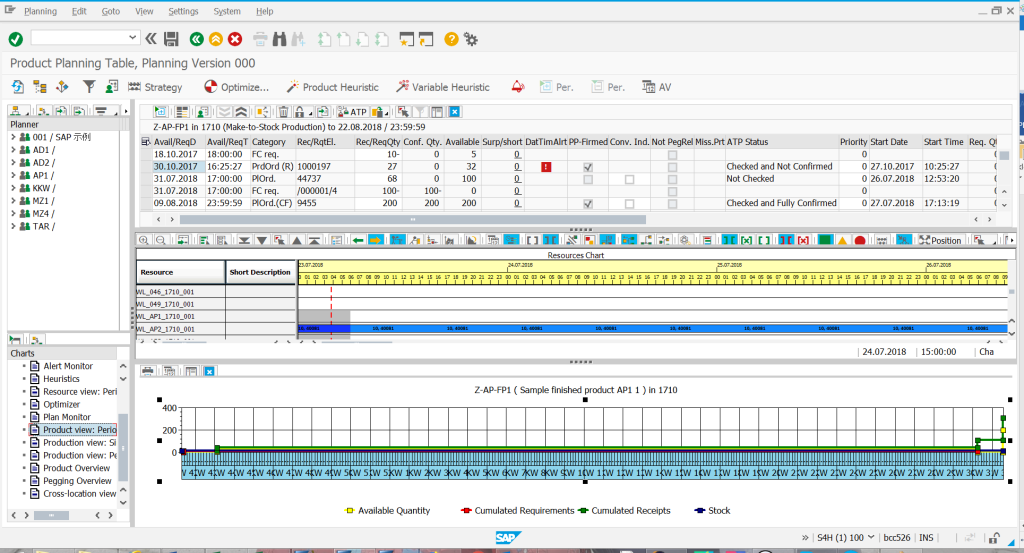
Product planning table
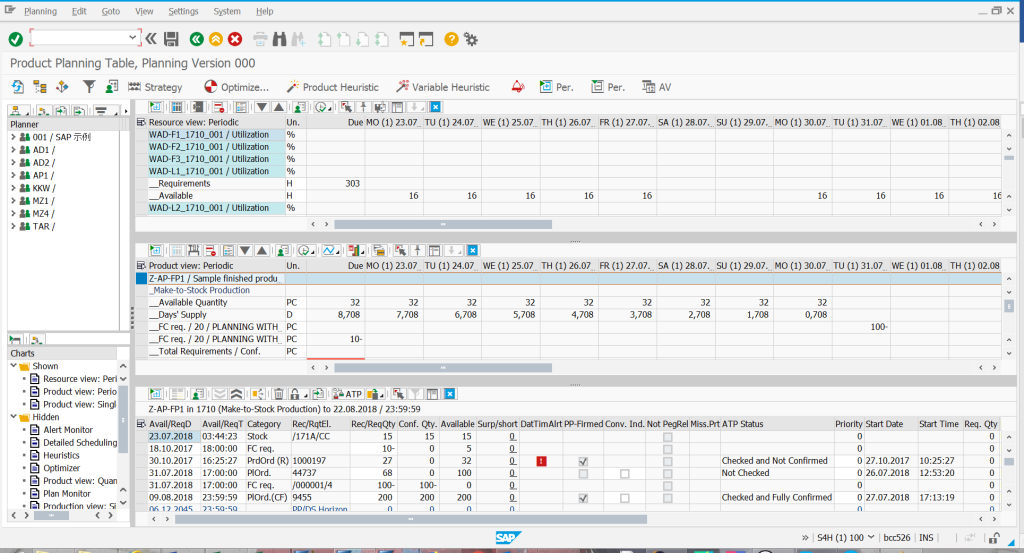
Product planning table
Product overview table (situation of inventory/demand for the whole group of products) – MD07 equivalent in SAP ERP. Additional options are e.g. the possibility to go to the Product Planning Table and Product View Table, verification of possible problems, messages related to the last main planning process, analysis of message sets generated by the alert monitor.
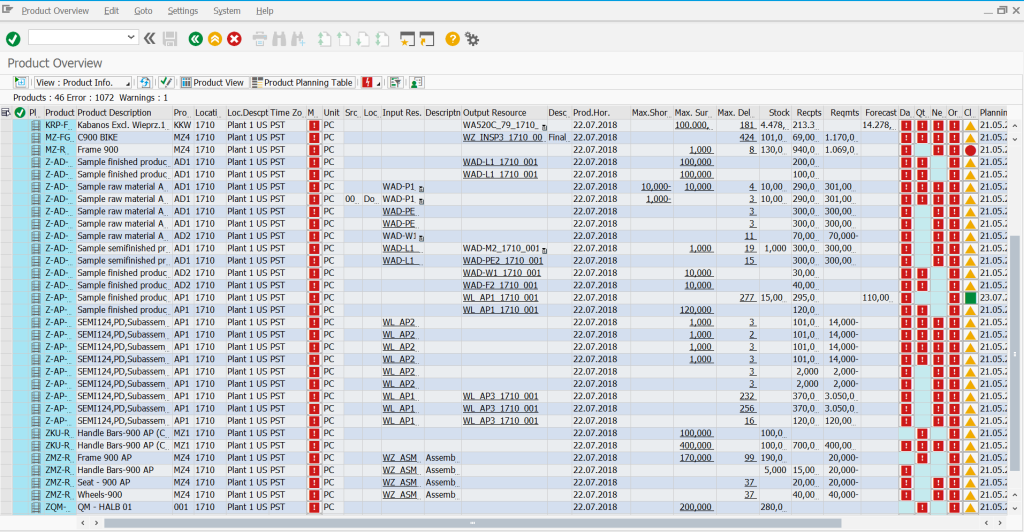
Product Overview table
Resource planning table – in a very simple way the equivalent of MF50/CM02 in SAP ERP. The main additional features are the ability to analyze the demand for production capacity in relation to the available capacity and the ability to schedule a production queue on a given selected resource. The planner can use scheduling heuristics, verify resource planning strategy, add downtime/breaks to the resource availability plan. The system displays information about the availability and load of a resource as well as a detailed list of operations and orders processed on a given resource.
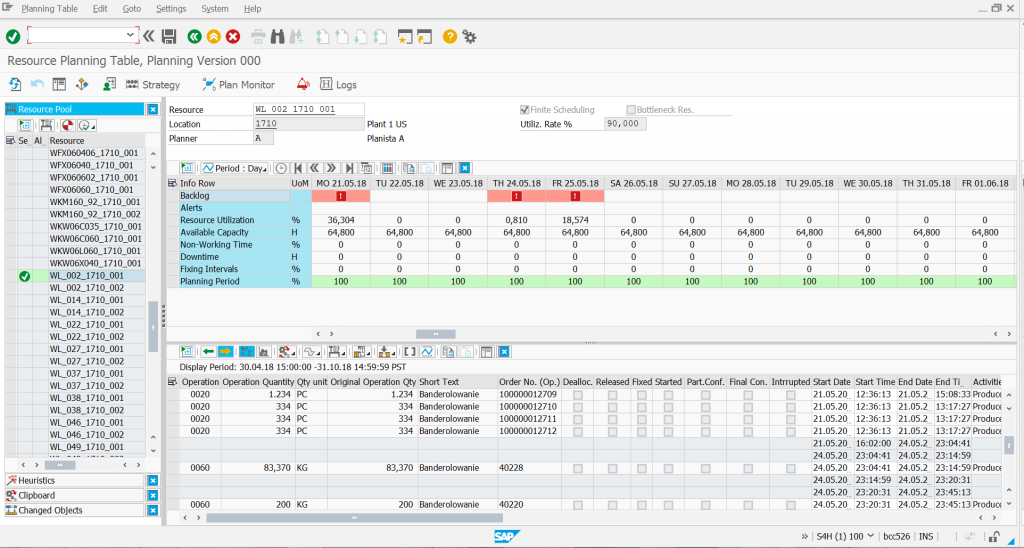
Resource planning table
Detailed planning table (including a runnable optimizer for refitting matrix, queuing orders) – equivalent of CM25 in SAP ERP. The planner can choose which elements will be analyzed on screen (graph of resources, production, order, operation, full use of resources). The functionality of the optimizer is also available (a tool for automatically searching for the optimal planning solution). The user can save the planning results as a simulation plan, which only after approval can be converted into the result of the operative planning.
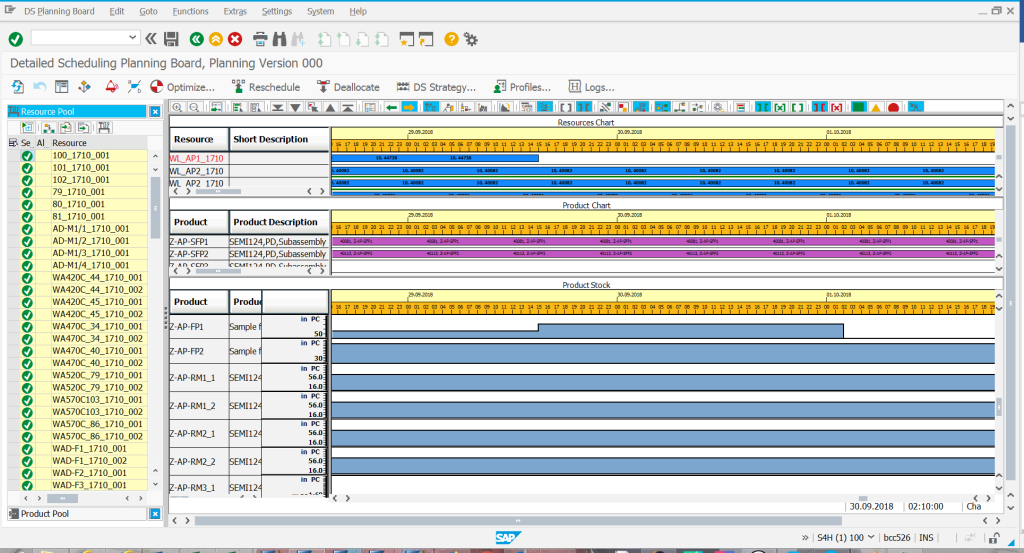
Detailed planning table
Alert monitor – flexible tool for verification and definition of planning alerts. Compared to a classic ERP system, the alert monitor offers much wider possibilities of setting the parameters according to which the system generates messages.
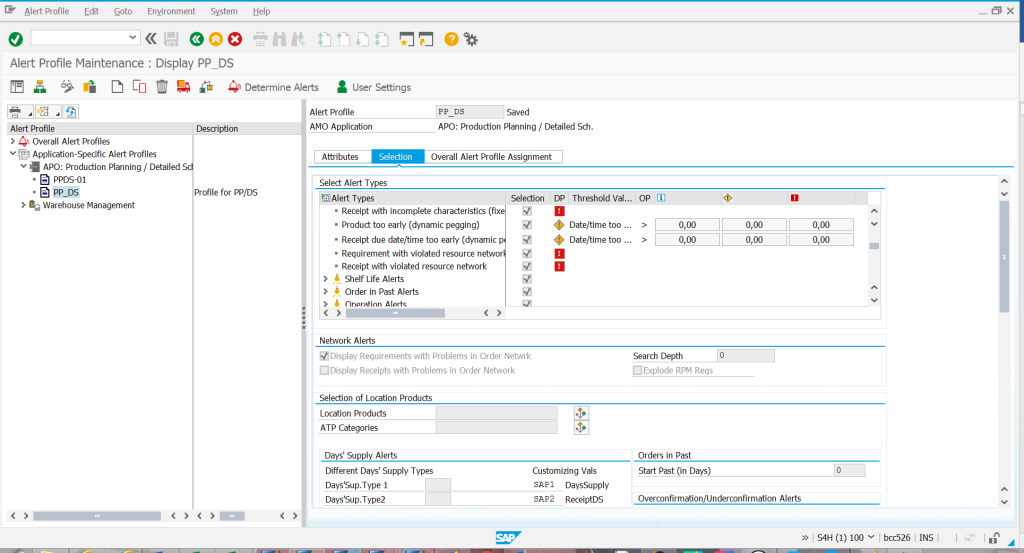
Alert monitor
Of course, the above mentioned functionalities and an attempt to relate them to standard transactions in SAP ERP and S/4HANA is a very big simplification. The aim is to show how much and how the planner’s tools and capabilities change after the PP/DS module is launched.
The most important thing is, for example, the possibility of using the product heuristics in the product overview table, where we can carry out the planning ourselves, verify its results, run the so-called variables of heuristics (the planner can select additional planning functions and run them). The plan will only be ‘put into effect’ once these results have been recorded.
In many transactions, detailed planning strategies are also used – where, for each strategy, it is defined how individual objects will be planned.
For example: searching for free time gaps, inserting operations, inserting operations with reduction, sequencing of operations by defined parameters, and also using the so-called optimizer. In strategies we also define how e.g. dependent objects are to be planned, how restrictively we define particular resources as finished resources (finiteness level), or whether the system can automatically select alternative resources (mode selection) and many others.
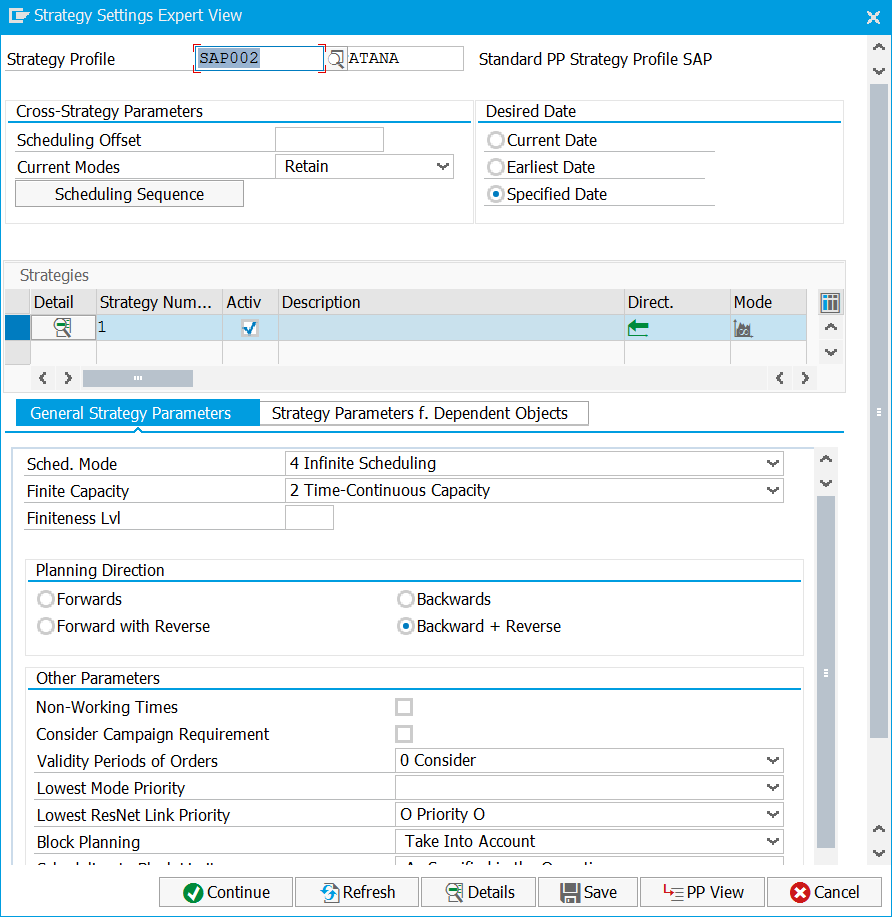
Strategy setting
Optimizer – a tool used in the above transactions, where after determining the appropriate validity (weights), the system may try to develop an optimal schedule on its own, taking into account guidelines related to the time and costs of refitting, preparation time, maximum delays and the sum of delays, withdrawals from the plan, changes in the product generation version (replacement of alternative resources).
The main difference between the optimizer and the heuristics is that the heuristics solves a specific problem, the task (e.g. performs multilevel scheduling), and the optimizer iteratively performs scheduling attempts, calculating deviations and differences in the cost of individual results, trying to select the optimal version. The settings of the individual indicators taken into account have a decisive impact on the outcome of this optimisation process. Due to the great complexity of planning problems, mutually exclusive limitations and assumptions taken into account, it is recommended that the optimizer is implemented starting from the possibly selected resources, departments, products, so that planners can work out the assumptions of the settings of particular parameters and can analyze the result before the optimizer is launched for the automatic planning of more resources/products.
New planning capabilities
With the PP/DS module in the S/4HANA SAP system, it opens up completely new planning possibilities for practically every company, so far reserved for larger players using the “large" APO supply chain optimisation system in SAP SCM. Additional new functionalities are an option, there is nothing to prevent the planning from using the already known SAP functionalities. In the case of new implementations, decision makers can rest assured that SAP S/4HANA will allow planners to develop functionalities and planning tools directly in the central system without the need to invest in potential external advanced planning systems (of APS-type).
Before you start implementing PP / DS, remember about:
- license verification – the PP/DS module is treated as a separate price list item,
- verification and installation of the so-called live cache (technical side of the Basis module),
- verification and installation of the optimizer (if these functions were to be used)
- execution of the basic configuration of the module.
The PP/DS module (production planning and detailed scheduling) in SAP S/4HANA is a dedicated solution designed in a special way for companies carrying out complex planning processes. Especially for those who have multilevel material specifications (BOMs) of their products and many alternative possibilities of performance and production start-up (the so-called production version). They carry out large scale contract manufacturing, especially for companies that are forced to carry out feasibility studies of the plan for many resources, including those planned as so-called finished resources – bottlenecks. The solution will also work where it is necessary to perform scheduling in an automated manner, plan simulations are also performed and where planners are looking for a tool allowing for using exceptions in planning. These may be companies from the metal and plastic processing industry, generally understood nesting machining or organisations that carry out more serial production but are looking for very advanced planning tools available directly in the SAP system.


