Anyone who has used a classic data warehouse, such as SAP BW, SAP BW/4HANA or analogous solutions from other vendors, knows how indispensable this tool is in a reporting environment based on multiple source systems or requiring complex data transformations. SAP Datasphere is undoubtedly distinguished from on-premise wholesale systems by three aspects:
- Intuitiveness and ease of implementation,
- scalability,
- view-based solution architecture.
All of the aforementioned factors not only make it possible to fully integrate data from different source systems, but also make implementing as well as using SAP Datasphere extremely easy. Much of the work involved in modeling or sharing data in SAP Datasphere can be done by key business users, not just consultants or IT staff.
The article is divided into four parts. They describe the source systems, how to transform data or how to cooperate and share information between users. The last part shows why the new-look data warehouse shows lower implementation costs and features easier and faster implementation than classic solutions.
Source systems
SAP Datasphere allows you to connect to source systems using 31 connection types. They enable data retrieval from both on-premise systems and cloud-based solutions. Supported source systems include:
- SAP systems: S/4HANA, ECC, from which data can be retrieved directly from tables, extractors and CDS views;
- data warehouses: SAP BW, SAP BW/4HANA;
- other SAP systems: SuccessFactors, Fieldglass, Marketing Cloud;
- cloud-based solutions: Google, Microsoft Azure, Amazon;
- databases: SAP HANA, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle and others;
- OData services;
- flat files.
At this point, it is worth noting that the source of data for SAP Datasphere can be not only new or relatively modern source systems. In the case of SAP ECC, we were also able to successfully acquire data from older environments, such as SAP ECC 6.0 in SAP ABAP 7.0.
By design, SAP Datasphere is largely view-based, and data does not need to be physically stored in a data warehouse to be used effectively for reporting. The configuration of data sources can be based largely or entirely on remote tables. Undoubtedly, the advantages of such a solution are always up-to-date data, which does not have to be regularly imported from source systems, as well as the lack of data redundancy, saving of memory resources and unification of permissions.
The cyclic import of data into the SAP Datasphere warehouse and the creation of data processing chains also continue to be supported. This is especially important for legacy source systems based on a database with lower performance.
Data modeling
The data modeling area in SAP Datasphere is divided into two sections:
- Data Builder allows you to create tables, views, merge data, and define task chains. Views can be created using a graphical interface or classic SQL queries. Reference is made to tables, views or extractors located on the side of the source systems;
- The Business Builder is primarily used to create dimensions, models or data sets that are consistent from a business perspective. Objects created in this section use what has already been implemented in the data builder section. Data permissions are also configured in this section.
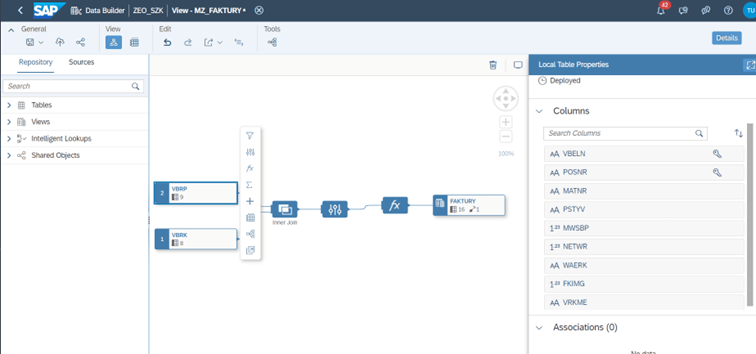
The graphical interface greatly facilitates the creation of individual data models and their transformation. In particular, with its help it is possible to define:
- Data filtering – using, among others, numeric, text or date functions with fixed or parameter assignment of values;
- Projection – that is, limiting the number of columns displayed;
- new calculations – including new dimensions, limited indicators and formulas, as well as currency conversion;
- data aggregation;
- Combining data – using union and join operations (all types);
- other, more advanced features.
At each stage of modeling, it is possible to preview the data so that modifications can be monitored in real time. Since the vast majority of modeling is based on views, the preview of data is available immediately, without having to reload it.
The created views or analytical collections can be shared with other users and externally. Thus, they can be a source of data for other systems or a basis for creating reports on the side of SAP Analytics Cloud and dedicated environments of various vendors.
SAP Datasphere
– data warehouse in the cloud
- SAP Datasphere pozwala połączyć się z systemami źródłowymi z użyciem 31 typów połączeń. Pozwalają one na pobieranie danych zarówno z systemów on-premise, jak i rozwiązań opartych na chmurze
- Data Builder umożliwia tworzenie tabel, widoków, łączenie danych, a także definiowanie łańcuchów zadań
- Business Builder służy przede wszystkim do tworzenia wymiarów, modeli lub zbiorów danych spójnych z punktu widzenia biznesowego
- Tworzenie modeli danych i ich transformacja odbywa się w interfejsie graficznym
- Architektura SAP Datasphere jest oparta na tzw. przestrzeniach (space)
Cooperation and powers
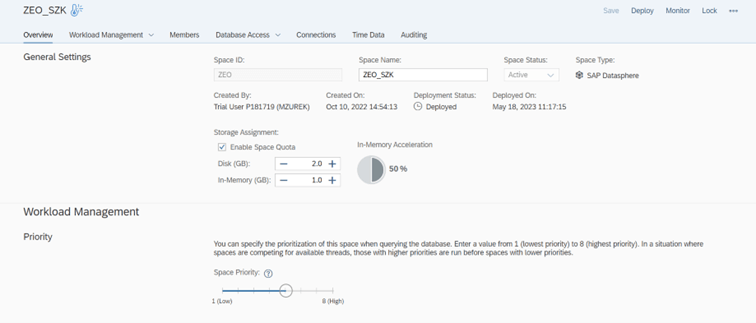
SAP Datasphere architecture is based on so-called spaces (spaces). Each space is assigned memory resources and users who have access to it. Connections to source systems are also defined at its level. It is worth noting that objects between spaces can be shared, so that created and running models are available to other users of the data warehouse. In SAP Datasphere, spaces are the basis for separating working environments for different project teams.
In addition to assigning users to individual spaces, it is of course possible to configure permissions. In SAP Datasphere, the creation of permission scenarios is available in the business builder section. Based on these, you can limit the data available to users to specific values of individual dimensions, such as a particular plant. It is also possible to create permission roles that grant users access to read or change particular types of objects in SAP Datasphere.
Implementation costs and scalability
The implementation of SAP Datasphere is much more attractive cost-wise than was the case with classic on-premise data warehouses. Two primary factors contribute to this:
- SAP Datasphere is a cloud solution, which means there are no expenses associated with the purchase and configuration of the corresponding servers or databases. In this regard, the only cost is the subscription.
- In SAP Datasphere, unlike SAP BW, it is not necessary to create individual objects before loading data. For example, in classic SAP BW, loading master data for a material involved defining the material feature on the warehouse side, along with defining the data type of its individual attributes. It was also necessary to define an appropriate data flow including transformation, infopackages or DTP processes. In the case of standard objects, a large part could be activated from the so-called BI Content. Still, the implementation of a classic SAP BW warehouse was much more time-consuming than it is today with SAP Datsphere.
Basing SAP Datasphere’s data warehouse on the cloud also translates into its easy scalability. If it grows, it is not necessary to incur additional expenses related to increasing available resources, but only to purchase an additional subscription that allows storing more data.
Having outlined the advantages and features of SAP Datasphere, the question may arise, what about existing, perhaps extended SAP BW or SAP BW/4HANA systems? The investments made so far in implementing the solution need not, and should not, be wasted. SAP Datasphere allows you to migrate existing data flows using the BW Bridge tool.
All this makes SAP Datasphere seem an attractive solution for both existing users of wholesale systems and those who feel the need to implement an environment that integrates data from different source systems, but so far, due to the complexity of implementation and high cost, do not yet have such a solution.
The user-friendly interface, ease of implementation and management, as well as extensive data transformation capabilities are undoubtedly SAP Datasphere’s differentiators from other data warehouses. In the era of computerization, data analysis using an increasing number of sources seems to be a necessity in order to make the right decisions quickly and remain a competitive organization in a given market.